Squint Surgery
Squint, or strabismus, is a condition where the eyes do not align properly. This misalignment can occur due to muscular imbalance, nerve issues, or refractive errors, leading to visual disturbances such as double vision or reduced depth perception. Squint surgery is a specialized procedure aimed at correcting this misalignment to restore normal binocular vision and improve aesthetic appearance.
Indications for Squint Surgery
Squint surgery is recommended for patients with:
– Congenital or acquired strabismus
– Significant cosmetic concerns
– Diplopia (double vision) affecting daily activities
– Unsuccessful non-surgical treatments such as glasses or vision therapy
– Binocular vision impairment
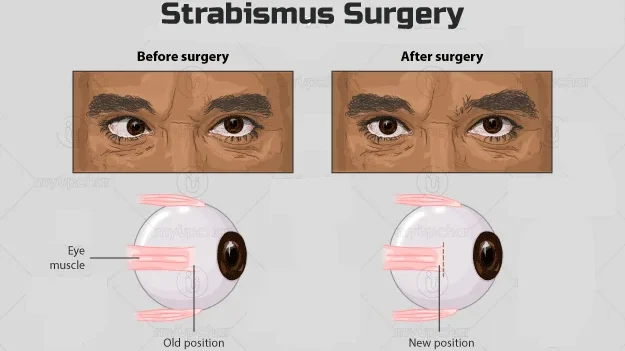
Procedure
Squint surgery involves the adjustment of extraocular muscles to realign the eyes. The procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia and typically lasts 30-60 minutes. Key steps include:
1. Muscle Strengthening or Weakening: The surgeon either shortens (resects) or repositions (recesses) the affected muscle to restore alignment.
2. Adjustable Sutures (if required): In some cases, adjustable sutures allow postoperative refinement of eye positioning.
3. Recovery & Follow-up: Patients are usually discharged the same day. Mild discomfort and redness subside within a few weeks. Regular follow-ups ensure optimal healing and alignment.
